The Omega Classification
|
|
|
|
-
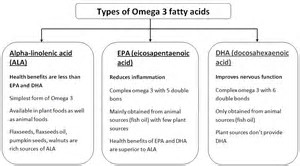
The Omega Classification
- Many fatty acids are now being given an Omega classification, eg Omega-3 or Omega-6. All this does is to provide a means of identifying the whereabouts of one of the double bonds in an unsaturated fatty acid. The position of the double bond is indicated relative to the carbon atom that is farthest away from the C))H (acid) group. This carbon is said to be in the Omega position.
|
|
 |
 |
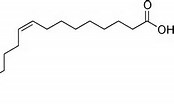
- Palmitoleic Acid
 |
 |
 |
 |
- Fatty Acids
- In the above sample, as the COOH group is on the right, the carbon atoms have been numbered from the extreme left, counting that carbon atom as number1.
- So, Omega 7 means the double bond lies between the 7th and 8th carbon atom counting from the left. This shorthand method does not tell you how many bonds there are in an unsaturated fatty acid, merely where, from the left, the first one lies: there may be more, but this system does not reveal that.
The List of Saturated and Unsaturated Fatty Acids Can Now Be Shown As:
| Former Name | Modern Name | Symbol |
| lauric | dodecanoic | C12:0 |
| myristic | tetradecanoic | C14:0 |
| palmitic | hexadecanoic | C16:0 |
| stearic | octadecanoic | C18:0 |
| arachidonic | eicosanoic | C20:0 |
| behenic | docsanoic | C22:0 |
| lignoceric | tetracosanoic | C24:0 |
| oleic | octadecanoic | C18:1 omega-9 |
| gadolei | 11-eicosanoic | C20:1 omega-9 |
| erucic** | 13-docosenoic | C22:1 omega-9 |
| cetoleic | 11-docosenoic | C22:1 omega-11 |
| linoleic* | 9,12,15-octadecadienoic | C18:2 omega-6 |
| alpha-linolenic | 9,12,15-octadecatrienoic | C18:3 omega-3 |
| gamma-linolenic | 6,9,12-octadecatrienoic | C18:3 omega-6 |
| dihomo-gamma-linolenic | 8,11,14-eicosatrienoic | C20:3 omega-6 |
| arachidonic | 5,8,11,14-eicosatetraenoic | C20:4 omega-6 |
| timnodonic | 5,8,11,14,17-eicosapentaenoic | C20:5 omega-3 |
| clupanodonic | 4,7,10,13,16,19-docosahexaenoic | C22:6 omega-3 |
- **erucic acid is considered to be carcinogenic
- *linolenic acid exists in two isometric forms, alpha (a) and gamma (Y)
- Reference: Carrier Oils For Aromatherapy And Massage: Len Price with Ian Smith and Shirley Price.
Articles-Most Read
- Home
- Contact Us
- Coconut Oil-2
- Absorption Ratings for Carrier Oils
- Cold Pressing Method
- What are Essential Fatty Acids
- Cherry Kernel Oil
- Fixed Oils and Skin Penetration
- Hempseed Oil
- Almond Oil
- Cocoa butter
- Camelina Oil
- Antibacterial Effects Of Carrier Oil
- Coconut Oil
- Lime Blossom Oil (macerated)
- Carrot Oil, Wild Carrot Oil (macerated)
- Apricot Kernel Oil
- Kukui Nut Oil
- Jojoba Wax
- Pumkin Seed Oil - Cucurbita maxima, C. pepo
- Passion Flower OIl (Macerated)
- Hydrocotyle Oil (macerated)
- Palm Kernel Oil
- Rapeseed Oil - Carrier Oil
- Nutrients
Who's On Line
We have 141 guests and no members online
Articles-Latest
- How to Make Homemade Olive Oil: A Step-by-Step Guide
- 20 Evidence-Based Aloe Vera Oil Benefits For Skin, Hair & Health
- Peanut oil - Cold pressed - Are There Health Benefits? How To Make
- What Are the Health Benefits of Black Seed Oil?
- Comfrey oil Infused
- Chamomile Flowers Infused Oil
- Calendula Flowers Infused Oil
- Arnica Flowers Infused Oil
- How To Make Herb-Infused Oils
- DIY avocado oil for healthy skin
- How To Make Coconut Oil
- 8 Benefits of Mustard Oil, Plus How to Use It
- SHOREA STENOPTERA SEED BUTTER
- Shea Butter- 7 Amazing Benefits Of Shea Butter
- Monoi Oil For Hair & Skin
- Mango Seed Oil
- Cohune Oil Is The Next Big Thing
- Brazil Nut OIl
- 7 Impressive Benefits Of Allspice
- Camelina Oil Benefits, Uses, and Side Effects