Definitions and Terminology




-
Definitions and Terminology
- Fixed Oils and Essential Oils - There are distinct differences between fixed and volatile plant oils.
- The plant oils used as carriers in aromatherapy and massage are referred to as 'fixed' oils because they do not evaporate.
- Plant essential oils do evaporate because they are volatile.
- Fixed oils leave a permanent oil mark on paper because of their lubricating quality and non-volatile nature.
Essential oils do not leave an oily mark on paper, although any colour present will leave a stain.
Fixed oils are not soluble in alcohol
Essential oils generally are soluble in alcohol.- In general, fixed oils are miscible with ether, chloroform and petroleum spirit.
- Essential oils dissolve easily and completely in fixed oils in all proportions; unscrupulous suppliers sometimes make use of this fact by using fixed oils to dilute essential oils in order to deceive unwary buyers.
- Lipids - Chemically speaking, fixed oils are classed as lipids. This is a diverse family of compounds found naturally in plants and animals, and the term encompasses not only oils but also fats.
- Although their structures are similar, at normal room temperatures (15C) fats are solid and oils are liquid.
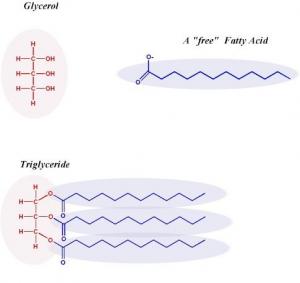
- Triacylglycerols - Fats and oils are formed when a special type of alcohol called glycerol reacts with a particular type of organic compound known as a fatty acid.
- Fatty acids all have a long hydrocarbon chain (typically)containing 16 or 18 carbon atoms) attached to the carboxyl group (-CooH).
- Some of them contain double bonds and are said to be unsaturated, whereas those without double bonds are referred to as saturated.
- The resulting compounds are triacylglycerols, also known as triglycerides, and a variety of these are possible. in the above chemical formula R',R" and R2"' represent chains of carbon atoms.
- Simple triacylglycerols are those in which R', R" and R2 are the same, ie three molecules of the same fatty acid have reacted with one molecule of glycerol).
- Complex triacylglycerols are those in which R', R" and R" are different. Perhaps not surprisingly, naturally occurring triacyl-glycerols are all complex.
- Triacylglycerols feature in our diet, and we digest them by utilising a lipase enzyme to reverse the above reaction.
- This process is called saponification, and is the way in which fatty acids are made available for us in our bodies.
- Mineral Oils - Mineral oils are hydrocarbons of high molecular weight and therefore a different class of compound from the triacylglycerols and lipids of vegetable origin.
- Mineral oils are not broken down by the body's digestive system and because of this have no nutritional value.
- Mineral oils - mineral oils are also oily and greasy, but they are not used in massage they have a tendency to clog the pores.
- However, because of these pore sealing qualities they, are used on Babie's bottoms, to help prevent the intrusion of urine, thus reducing the risk of nappy rash.
- Reference: Carrier Oils for Aromatherapy and Massage: Len Price with Shirley Price
Articles-Most Read
- Home
- Contact Us
- Coconut Oil-2
- Absorption Ratings for Carrier Oils
- Cold Pressing Method
- What are Essential Fatty Acids
- Cherry Kernel Oil
- Fixed Oils and Skin Penetration
- Hempseed Oil
- Almond Oil
- Cocoa butter
- Camelina Oil
- Antibacterial Effects Of Carrier Oil
- Coconut Oil
- Lime Blossom Oil (macerated)
- Carrot Oil, Wild Carrot Oil (macerated)
- Apricot Kernel Oil
- Kukui Nut Oil
- Jojoba Wax
- Pumkin Seed Oil - Cucurbita maxima, C. pepo
- Passion Flower OIl (Macerated)
- Hydrocotyle Oil (macerated)
- Palm Kernel Oil
- Rapeseed Oil - Carrier Oil
- Nutrients
Who's On Line
We have 55 guests and no members online
Articles-Latest
- How to Make Homemade Olive Oil: A Step-by-Step Guide
- 20 Evidence-Based Aloe Vera Oil Benefits For Skin, Hair & Health
- Peanut oil - Cold pressed - Are There Health Benefits? How To Make
- What Are the Health Benefits of Black Seed Oil?
- Comfrey oil Infused
- Chamomile Flowers Infused Oil
- Calendula Flowers Infused Oil
- Arnica Flowers Infused Oil
- How To Make Herb-Infused Oils
- DIY avocado oil for healthy skin
- How To Make Coconut Oil
- 8 Benefits of Mustard Oil, Plus How to Use It
- SHOREA STENOPTERA SEED BUTTER
- Shea Butter- 7 Amazing Benefits Of Shea Butter
- Monoi Oil For Hair & Skin
- Mango Seed Oil
- Cohune Oil Is The Next Big Thing
- Brazil Nut OIl
- 7 Impressive Benefits Of Allspice
- Camelina Oil Benefits, Uses, and Side Effects